Best ERP Software for Your Business
Best ERP software are Oracle NetSuite, Microsoft Dynamics, SAP ERP, TallyPrime, and DataNote. It simplifies your entire business and keeps all data in one place. As a result, it allows for a more efficient, accurate, and data-driven work environment.



Connect With Your Personal Advisor
List of 20 Best ERP Software
Until 31st Mar 2023


ERP Software: In Detail Guide
ERP software is an industry acronym for Enterprise Resource Planning software. It refers to a comprehensive system that manages all the software pieces that you might need to run your business operation in a single place.
In simple terms, it automates and integrates business core functionalities to increase productivity. The purpose of an ERP system is to create a smooth flow of information that is always in sync with all departments. It allows employees across all divisions to have access to the same information. Thus, they can use the same data as a point of reference.
According to the IT Priorities survey, 53% of businesses name ERP as their priority investment. They are discovering the versatility that the platform has to offer. It provides tools that make every business activity seamless throughout all departments.
A Brief History of ERP
The term ERP was first used in 1990 by Gartner. But it’s fair to say that its roots date back to the sixties. It was when a researcher at IBM created the concept of material requirement planning or ‘MRP.’
The concept was developed for the manufacturers to assist them in their planning process. It provided a method of planning the quantities of materials required for production. And thus, ensuring that the materials arrived on time so that they can keep production running.
Eventually, MRP grew to encompass more manufacturing processes. People started to call it MRP-II or Manufacturing Resource Planning. It added capacity planning, scheduling, and forecasting to material requirements planning. This further smoothened the production plan.
By 1990, these systems began to include other operational processes as well. Some of these included back-office functions like accounting systems and human resources. It ultimately set the stage for ERP as we know it today.
Since then, ERP has continued to evolve. It has incorporated business intelligence and front-office functions into the system. Even though the ‘E; in ERP stands for ‘enterprise,’ more and more companies of varying sizes are implementing ERP systems into their business.
Types of ERP System
There are hundreds of ERP software available on the market. These systems can be categorized in many ways based on their functionalities, tier-based, versions, and more.
Typically, ERP systems are classified in tiers based on the size and complexities of the industry served. It includes:
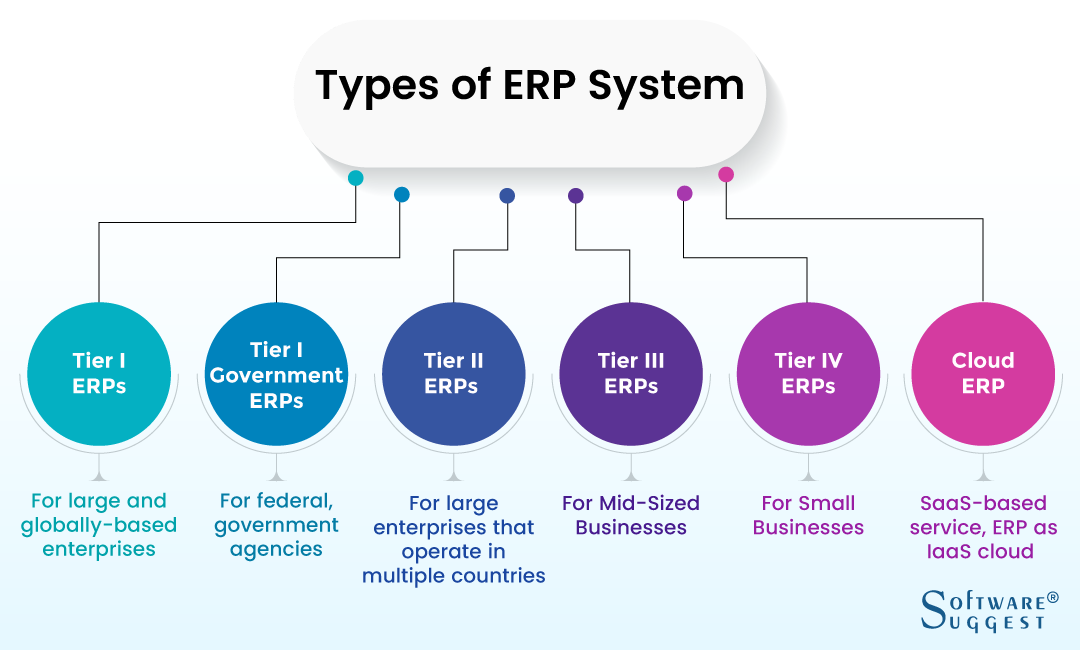
1. Tier I ERPs
Tier I EPRs are designed to serve large and globally-based enterprises. These solutions can adapt to various processes across different industries. Also, they are highly customizable to fit into the organization’s exact needs.
To comply with international standards, it can handle issues related to currency, postal codes, accounting rules, and more. Oracle and SAP have been considered Tier I ERPs for decades.
2. Tier I Government ERPs
The only difference here is that it supports federal, government agencies. These vendors clearly understand the nuances of how these large government organizations work. And accordingly, they design a system that follows all their rules and regulations. Some of the names are CompuServe’s PRISM, SAP, and Oracle.
3. Tier II ERPs
Tier II EPRs can again support large enterprises. Companies that operate in multiple countries but lack global reach can make use of Tier II ERPs. It can be used for standalone entities or business units of large global enterprises. There are around 25 to 45 vendors that fall into this category some of which include Abas, Epicor, Deltek, etc.
4. Tier III ERPs
Tier III ERPs offer solutions for mid-sized enterprises. They are limited to a handful of languages and currencies as compared to Tier I and II systems. Tier III vendors comprise of Blue Link, Technosoft Corporation, and more.
5. Tier IV ERPs
Tier IV ERPs are basically what we call ERPs for small businesses. It provides solutions for sales and order management, or human resources, but not for full warehouse management. A scaled-down ERP system is ideal for small business who doesn’t need a fully integrated system but only pared-down features. Moreover, ERPs for small businesses are generally free and open source.
Sage 300 ERP and Altas are a few names in the Tier IV ERPs category. Apart from the complexities of the system, ERPs can also be classified into web-based or cloud ERP. Instead of running advanced enterprise resource planning systems on computers, some vendors decided to go with web-based solutions.
In the recent past, ERP software vendors have created a cloud version of their software. The vendors charge a subscription fee (monthly or yearly) for accessing the software. They store data over the internet. The advantage of Cloud ERP is that you can access the data from anywhere with an internet connection.
However, not all Cloud ERP operates in the same way. They can be classified into two types:
1. SaaS-based service
With these ERPs, all customers operate on the same code base. The users can configure but not customize the code. The users don’t get access to the source code.
2. ERP as IaaS cloud
Here, enterprises can’t use ERP as a service if they want to rely on custom code. However, if they still wish to operate in the cloud, they need to move to an IaaS provider. They shift their servers to a different location.
Modules of ERP System
ERP software provides the tools needed to make business activities seamless throughout all departments. It’s a combination of small modules integrated into one system. These modules automate all the processes and let you run your business smoothly. From procuring raw materials to finished products, marketing, and sales, it covers all aspects of your business. You will find thousands of ERP vendors. Though the implementation platforms may be different, there are basic modules of ERP which can be found in any ERP System. A list of a standard set of modules includes:
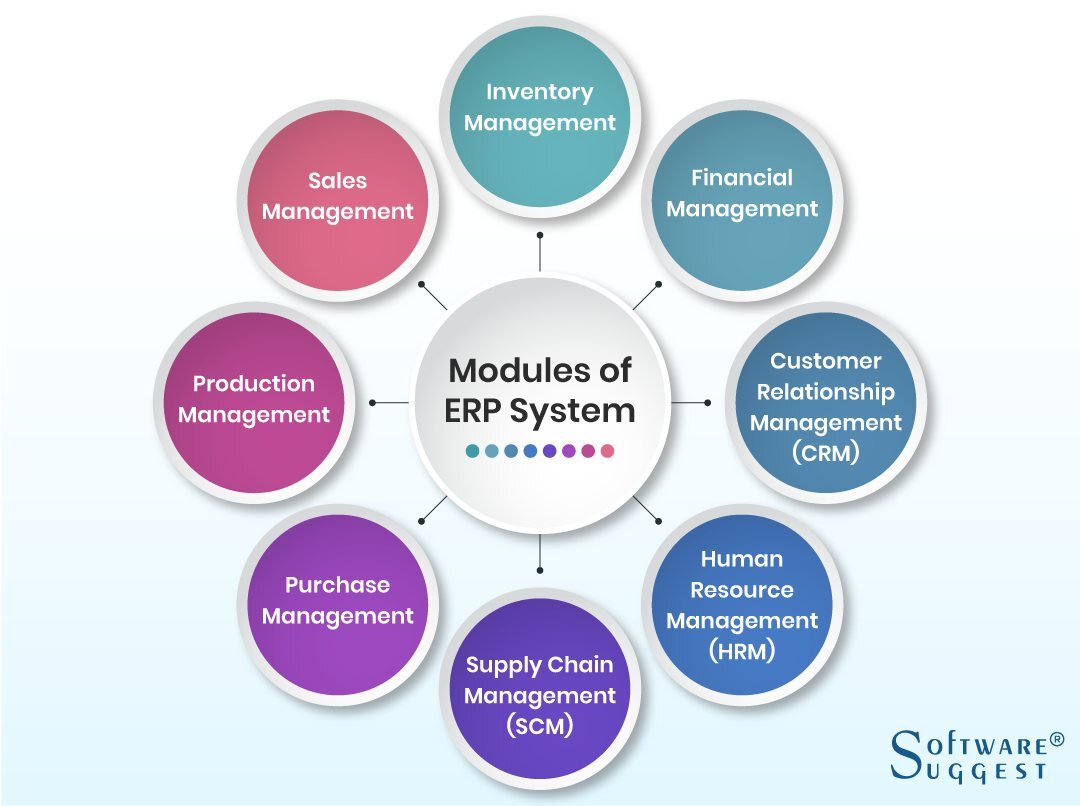
1. Inventory Management
The inventory module is used to track the stock items and help measure other inventory goals. It is also known as a material management module. Each piece has a unique serial number, which is used to keep a record of things and trace their location.
For instance, a company that deals with installing hard disks can use an inventory system. It will help keep track of how many hard drives have been installed, where they are installed, etc.
In short, it includes functionalities like stock replenishment, inventory control, etc.
It is closely linked with the purchase module of ERP.
2. Financial Management
With the help of the financial module, you can gather any financial data on one click. It takes care of all your account-related transactions. That includes accounts payable and receivable, general ledger, balance sheet, tax management, etc.
The financial module manages the total capital inflow and outflow of your business.
3. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM software is particularly important as it helps boost sales performance through better customer service. It seamlessly manages prospects, leads, and customer issues. Thus, it results in increased profit per capita.
The module provides complete detailed information of your customers. It consolidates data like social media activities, past interactions with support reps, and purchase details. This information provides an opportunity to build a healthy relationship with your customers.
There may be an integration of the CRM with the sales module to enhance sales opportunities.
4. Human Resource Management (HRM)
HRM module helps to carry out the HR-related tasks efficiently. From maintaining employees’ databases to tracking time, creating job profiles, and more, HRM does it all. It may also include performance review and the payroll system.
In an ERP setup, it is closely linked with the financial system. So that it can help manage wages, payment records, etc.
Also, the travel ERP module can keep track of employees’ travel expenses and reimbursement.
5. Supply Chain Management (SCM)
SCM module manages every aspect of purchase order management. It handles the flow of items from manufacturers to consumers and vice-versa too. Standard functionalities of SCM includes:
-
Demand and supply management
-
Sales returns and replacement
-
Shipping, etc.
The module automates the entire supply chain function. One of its key features is that it is highly adaptive to sudden market shifts.
6. Purchase Management
The purchase module manages the task of procuring raw materials or items. It consists of functions like:
-
Supplier listing
-
Supplier & item linking
-
Sending and receiving sending a quotation request to vendors
-
Analysis of quotations
-
Preparing purchase orders
-
Tracking the purchase items
-
Making Good Receipt Notes
As such, it is integrated with the inventory and production module for updating stocks.
7. Production Management
Production management is of great importance, especially ERP for the manufacturing industry. It helps smoothly manage the production process. From product planning to procure materials, and product forecasting, it does it all.
Some of its key functionalities are:
-
Shop floor control
-
Generating bills for materials
-
Manufacturing schedule
-
Distribution planning
-
Production reporting
Moreover, this module is linked with SCM and inventory modules.
8. Sales Management
As the name suggests, the sales management module handles the sales workflow. It includes product inquiries, sales orders, and invoices. A more advanced ERP would also be able to tackle taxation and feature shipping trackers.
The CRM and sales modules are integrated to speed up the sale cycles and generate more leads.
ERP can efficiently automate and streamline the business operations of the organization. You can choose and customize the above modules depending on your company’s needs.
Benefits of ERP Software
In this cut-throat competitive world, business houses want to become more efficient. They want to ensure regulatory compliance, improve customer service, and optimally utilize resources. But how do you achieve that?
ERP system is a solution to all your business operating needs. To name a few, it can help save time and material costs, achieve tight shop floor control, and much more.
Many business units have achieved their goals time after time by implementing an ERP solution. And if you think your business can’t afford ERP, you are wrong. There are ERPs for small companies as well. You need to choose the right vendor.
Some of the main benefits of an ERP system involve:

1. Improves Efficiency
It can be hard to run a business if every typical process needs to be enforced manually. ERP dramatically reduces the need for manually entering information by automating the tasks. Not only that, but it also helps eliminate several repetitive processes.
Consistency is the key to success in any business industry. ERP creates that consistency by streamlining workflows and thus, improving efficiency. In short, your employees can focus on more value-added tasks. And the ERP system can take care of all the mundane work.
2. Provides Better Customer Service
For any business to grow, it’s essential to achieve a higher rate of customer satisfaction. Any basic ERP system should be able to deliver client information from a single screen. This allows the sales department to keep track of its workflow. That includes order inquiries, billing information, and purchase history records of their clients. As a result, it helps generate more leads and increases profit per capita.
3. Delivers Meaningful Reports With Ease
Manually handling spreadsheets for different departments is prone to errors. Without an efficient ERP system in place, the chances are that your business data may not be accurate.
ERP software gives you the ability to analyze the information collected from various departments. Thus, it results in full-fledged insightful reports which are entirely error-free. It helps in making better decisions as it delivers transparency across all departments.
4. Enables Growth
Despite having a significant workforce, entering data manually can be time-consuming. You are more prone to error and also slow down the growth of the business.
To enable growth, using an advanced ERP system can help. It will allow you to manage your inventory and resource better. Plus, you will have access to reliable information all the time to make smarter business decisions.
5. Manages Compliances and Regulatory Needs
Most industries require to meet specific compliance standards for their products. Otherwise, it results in huge fines and customer dissatisfaction. If you want to avoid such a situation, employing an ERP system can help.
An ERP system keeps detailed records of all activities for audit. You don’t need to track the whole production process manually. It ensures that all the methods comply with proper standards.
6. Conducts Accurate Inventory Planning
Whether you are in the manufacturing sector or not, every business has a product or service to deal with. There are times when your physical count doesn’t match the perpetual inventory records. You may run out of stock. As a result, you face a delay in production and customer dissatisfaction.
You can avoid such situations by using an effective ERP system. With the help of ERP, you can have accurate access to inventory, reduce overhead, and more. Thus, you can have a smooth production process without any hassle.
7. Improves Decision-Making Ability
It’s true that with the help of ERP, numbers can be analyzed in real-time. An ERP system continually updates the information from across all departments. So any time you want to access the data, you are always presented with the latest reports.
Thus, it allows the management to take present-day decisions based on current data. Otherwise, they have to rely on quarterly or weekly reports. And the chances are that it might not be at par with the present-day situation.
Top ERP Vendors by Company Size Served
The global ERP software market size is expected to reach $71.63 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 8.5%. Since the 1990s, ERP systems have been a critical component of business operations. They have served vital functions like integration, collaboration, communication, and more.
But with cloud technology taking over the industrial realm, cloud-based ERP solutions have become more prevalent. A 2012-2013 research report from Gartner and Forbes suggests the following market share of ERP vendors.
-
SAP: 25%
-
Oracle: 12%
-
Sage: 6%
-
Infor: 6%
-
Microsoft: 5%
While new ERP system providers like PLEX Systems, Acumatica, Inc., and Epicor Software Corporation have made their way to the market, SAP, Oracle, and Sage remain to be the market leaders.
|
Enterprise |
Mid Sized |
Small Sized |
|---|---|---|
| SYSPRO | Sage Intacct | |
| Tally ERP9 | ||
| Sage 300 cloud | ||
| ERPNext | ||
Must-have Features of ERP Software
The purpose, scalability, and functionality of an ERP system will vary widely. However, there are some standard features of ERP software. Those are:

1. Real-Time Operations
One of the essential features of an ERP system is that it needs to operate in real-time. For instance, if an order is placed, the system automatically initiates a product availability query. And then, update the distribution schedule as well. Once the order is shipped, it sends out an invoice itself.
An advantage of it is that problems can be identified quickly, which gives the seller more time to rectify them.
2. Enterprise-Wide Integration
The primary purpose of any ERP system is to streamline the whole operational activity of a business. An ERP system allows for the seamless integration of different software operating from a single dashboard.
3. Common Database
In the earlier days, ERP had a common database for every department. It means every unit within the enterprise operated on a common data definition. However, things have changed a bit. Individual departments are required to conform to the approved data standards and editing rules.
You will find enterprises that continue to rely on a single ERP database. Whereas some prefer to split the physical database to improve performance.
4. User-Friendly Interface
A system can only be effective if it's an easy-to-use and friendly interface. It allows all the employees, including the non-tech savvy, to access the software easily. That means you can also save on training costs.
Another advantage of a consistent user interface is that it makes it look professional. There are times when vendors usually compromise with the interface in favor of speed. But with the new release of ERP systems, most vendors are restoring the consistent user interface.
5. Complete Process Automation
A sound ERP system will be able to automate every workflow of an enterprise. The system ensures that the data entry from all departments is regularly updated. And on top of that, it also speaks of accuracy and reliability as there is no room for errors.
As a result, you are automating tasks results in increased productivity and overall efficiency of the business. Moreover, complete automation of tasks motivates your employees more, as they can focus more on less repetitive tasks.
6. Security
Security is another important feature any enterprise resource planning software should have. An ERP system is where all the company’s information is stored. Despite an ERP having all the best features, it’s useless unless it’s secured. Whatever features you decide to choose, never compromise with the security factor.
Ideally, an ERP system should have a two-way authentication system. Top systems should also include a permit-driven architecture that allows the admin to restrict access for other employees.
Who Uses ERP Software?
ERP software has a lot of benefits to offer to all kinds of businesses. While ERPs were originally designed for manufacturing companies, they have expanded to many other industries.
Companies with streamlined processes can get orders out faster, satisfy their customers, and stay on top of the competition. All of it is possible because of the implementation of an ERP system. And that brings us to our next question.
1. Which Size Companies Benefit the Most From ERP?
If you think your company is too small to implement an ERP system just yet, you might want to reconsider.
Indeed, the larger, complex operations will have the most benefit by using an ERP. It might be difficult for them to operate without an ERP system in place. But in truth, a lot of small companies also have a lot to gain from an ERP system. This is because it’s not just about the size or complexity of your organization right now.
One crucial factor that determines the need for ERP is where you want or expect your organization to be in the future. If you have plans for your company to grow, ERP is a must. You might be doing fine without an ERP right now. But you can’t expect to grow without adjusting your business processes to scale.
Companies can’t manage all their process manually for a long time. As the customer base expands, they need to find ways to automate specific tasks if not all. Thus, one can be benefitted by implementing ERP in time.
2. Which Industry or Manufacturing Model Benefits Most From ERP?
An advanced ERP is open to customization based on an organization’s specific needs. That's why it’s possible for a wide range of industries and business models to benefit from the use of ERP.
Regardless of the complexities of a business, an ERP system helps streamline the operational process. It can easily manage supply chains, which results in the fast distribution of products in the market. Also, there are a few industries that have to maintain compliance.
For instance, the food and beverage industry, an electronics manufacturing company, or a medical device manufacturer. They all have to meet specific standards set by the government to manufacture the product. But the good news is all of these industries can easily maintain compliance with the help of ERP.
For any company, compliance is essential for better quality control. Whether your compliance maintenance is required by your industry or it's just a standard set by you for your customers’ satisfaction, either way, you need an excellent system to keep track of quality control management. And an advanced ERP will be able to help you with that.
In a nutshell, the right ERP software will scale to fit different sizes of companies and industries. Any manufacturer who would like to improve efficiency can benefit from ERP. And any company that thinks they can’t afford an ERP merely is wrong. You need to look for the right vendor. ERP is an affordable solution for every company and has a lot to offer.
Factors to Consider When Choosing ERP Software
An ERP solution that’s a perfect match for one company may not be a good fit for another. They are not equally created. It’s essential that you give careful consideration to both the selection of software and the vendor.
Selecting the right ERP system can seem quite a daunting task at first. But consider the five factors discussed below while purchasing, it will solve the problem for you.
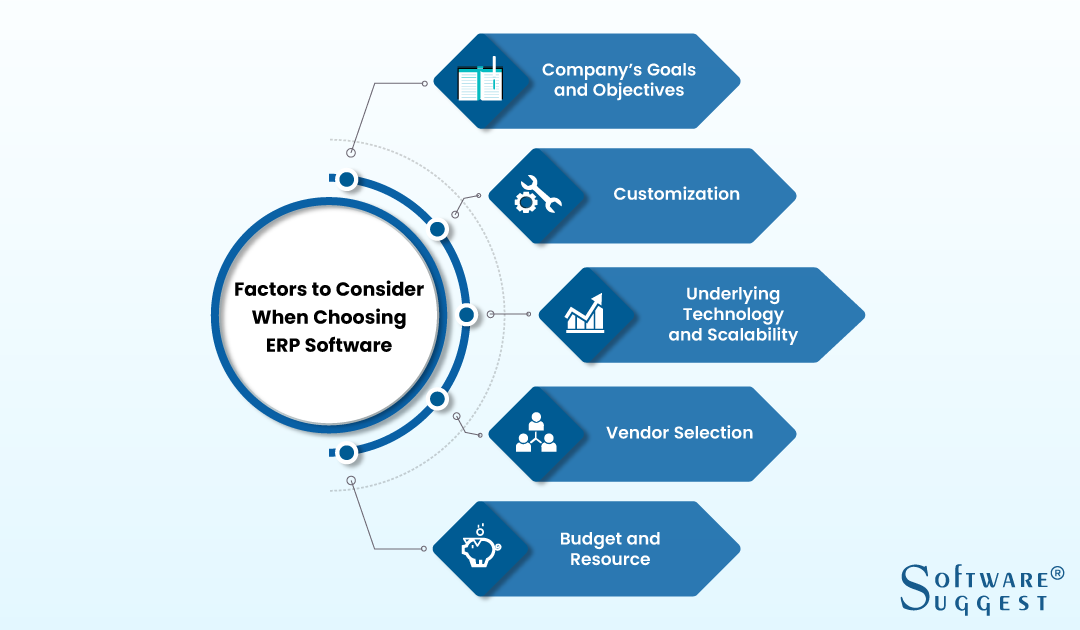
1. Company’s Goals and Objectives
The primary purpose of shifting to a new ERP system is to define the company’s goal.
Many companies envision improved performance and reduced costs. If you are planning to expand your business, you probably want to automate the redundant data entry task.
Or if you already have a system in place, it might need an upgrade to match your company’s growth. When you first implemented it, you might have focused just on maintaining customer relationships. Whereas now you need integration with inventory module and supply chain management as well.
Whatever the reason may be, pulling all the business workflows into one system can help achieve higher accuracy. Operating through a single database can save a lot of time and energy. And also, helps in making smarter business decisions.
2. Underlying Technology and Scalability
In the beginning, the technology of an ERP system wasn’t a matter of concern. The companies only had to care about software functionality. But time has changed. To operate an advanced ERP software, one needs to deploy a robust and diverse technology.
Thus, the cost of installing or upgrading to a new ERP system includes more than the price of the software. You need to calculate the lost time, training, and business disruption as well. Moreover, in case the technology is not at par, you might need to pay extra for that too.
That’s why always choose a system that is based on newer technology. It will save you the headache of continually planning to upgrade your system and make for a better investment.
3. Customization
You will find thousands of features in a single ERP system, but you might not need all. Don’t get confused.
For instance, you found a system that does everything. But it isn’t much compatible with your financial system. In that case, you can always have your ERP customized and integrate it with your existing software. But it would also mean extra cost of implementation.
The new ERP also allows individual departments to conform to the approved data standards and editing rules. Earlier, an ERP was designed to operate from a single dashboard. But with the newer ERP system, you can split the physical database to improve performance.
Therefore, always look for an ERP solution that comes with customization tools and configurable workflow. So that each department can define its own goals and set its parameters.
4. Vendor Selection
You might be surprised, but one of the biggest reasons why ERP projects fail has to do with the vendors. Most companies want to replace the current system because of vendor problems.
The company might have an adequate system in place — with few customization and upgrades. But it gets hard to operate without the right guidance and support from the vendor.
So what should you look for in a vendor? Few questions you can ask before picking up one:
(i) What kind of manufacturing do they specialize in?
It’s not necessary that vendors would be aware of the know-how of every industry. There has been a huge push to integrate ERP with financial systems in recent years. As such, most financial companies developed an ERP system without real understanding of manufacturing or production. That’s why it’s essential to differentiate between vendors who are manufacturing pros.
(ii) How much experience do they have with a specific kind of product or manufacturing method?
It’s wrong to assume that if the vendors have been around for a long time, you can partner with them. Not every vendor specializes in all kinds of industries. You need to know certain things like who their customers are.
(iii) What kind of support can you expect from the vendor?
This is the most crucial equation you need to have with any vendor. You will need support from your vendor, not just during the implementation period. But also after the project is over. Few things you should take care of before entering into any agreement with them:
-
Will they be there to help you through the implementation process?
-
How long will it take to set up the whole system?
-
How often can you reach out to them once the implementation is over?
-
What kind of training support do they provide to your teammates?
In short, you must know the kind of care and support they offer their customers. One best way to know that is by asking them to speak to their existing customers who are in a similar business. Ask them simple questions to understand how they feel about the vendors and their support.
And if the vendor refuses to share the customer’s number, you need to move to the next name on your list.
5. Budget and Resource
Not all ERP is priced the same. The highest-priced ERP can go as high as five times the cost of the least expensive system. The costs depend on the functionalities and complexities of the system.
Some companies need advanced functionalities that are built into a high-priced system. But not every company needs a complex system. ERP for small businesses can do away with less expensive built with minimal complexities. So don’t think that expensive is necessarily better. There is a different cost of running each type of system. So pick the one that fits your criteria and budget as well. ERP is an affordable solution for every company as long as they know how to choose the right system.
ERP Software Market Size, Share, Growth, and Forecast to 2025
The Enterprise Resource Planning software market is being estimated to amass a revenue of $56.8 billion by the year 2025. The Compound Annual Growth Rate of ERP software is an estimated 6.9% from the year 2016 to 2025. For the uninitiated, this growth in the market share of ERP has become feasible because of its plentiful advantages.
The finance business function contributed most to the market in the year 2018 and is being estimated to remain the same way in the coming years. The Human Resource module is also expected to grow at a very good rate. Apart from these two, the manufacturing industry also dominated the ERP software market share in the year 2018 and the same pattern is being expected in the coming years. This is due to the rise in the number of entrants in the garment, automotive, pharmaceutical, and electronics manufacturing markets.
Challenges Companies Face When Implementing an ERP Software

1. ERP Vendors
There are a plethora of ERP programs available in the market. Choosing the one which suits your organizational needs is what matters the most here. It can be a strenuous task to make this decision.
2. Ensuring commitment
The top management in every firm plays a vital role in making business decisions. Any form of disinterest from the senior managers may cause delays in operations.
3. Proper Training
Once an ERP program is implemented, bitterness amongst a few employees is almost inevitable. To avoid this, special training should be given to the employees so as to make them comfortable with the new changes so that the productivity of the firm increases and not results otherwise.
4. Managing the Project Properly
Needless to say, it is always a wise decision to assign the best employees of the firm the duty to implement the new program. This can be done if external help is not needed.
5. Cost of Implementation
Till the time the entire implementation process is complete, lots of redundant costs have been included. This happens because after the system gets installed, the company also has to bear the costs of updating the program.
6. Proper Testing
Testing the software means ensuring the fact that the software lives up to the expectations and desires of the organization. In case of insufficient testing, lots of expensive updating would be needed to be done.
7. Maintenance Cost
Good maintenance is mandatory for the software to run efficiently. This adds up to recurring costs for the firm.
Common Myths About ERP System
ERP system is gaining popularity among businesses. However, many myths are surrounding the implementation of an ERP system. Let’s break those common myths today.
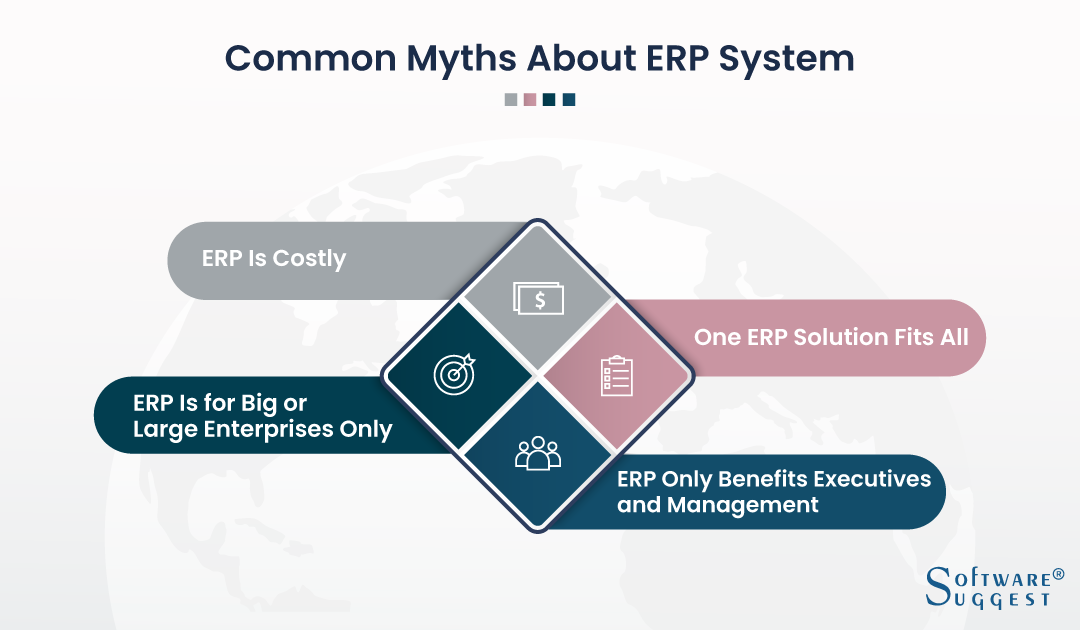
Myth #1: ERP Is Costly
You will find a range of ERP systems designed to serve different sizes and industries. Don’t necessarily get confused that expensive ones are better than low-priced ones. However, your focus should be on getting a comprehensive system that fits your company’s needs.
Even if it seems costly, the investment will only reap benefits for you in the future. Your return on investment (ROI of ERP) depends on the overall value derived from the system over time.
Myth #2: One ERP Solution Fits All
Certainly, not true.
Each ERP system is unique to its applications and interface. It’s essential to compare ERP solutions and select the best fit for your business requirements.
The need for a company that manufactures a variety of products will undoubtedly differ from those that produce only one product. Besides, a food and beverage industry's needs will vary from that of electronic device-making enterprises.
The functionalities and capabilities of an ERP system vary depending on the various business needs.
Myth #3: ERP Is for Big or Large Enterprises Only
When ERP was first introduced, it was solely for the big enterprises in the market. However, things have changed, and vendors are coming up with ERP solutions for small businesses too.
ERP solutions come in various shapes and sizes. Selecting the right ERP software is essential for longevity and effective implementation.
Myth #4: ERP Only Benefits Executives and Management
An ERP system in place benefits every employee involved in the organization. It provides vital information to the upper management for decision-making. Besides, it automates the workflows between departments which results in widespread sharing of information. The advantage of it is that you will have improved project planning and lower purchase cost.
Upcoming ERP Trends

Over the last decade, the ERP market has evolved fast. Vendors are now offering enterprise-wide solutions with advanced functionalities. Some of the future trends in the ERP market that will drive the growth are:
1. Mobility
Some ERP vendors are coming up with ERP solutions supported on mobile devices. That means you would be able to access your back and front office operation anytime and anywhere on any mobile device. Managers and workers will be able to manage the critical operations on the go seamlessly.
2. Demand for Cloud-Based Solutions
Over the next decade, cloud-based ERP solutions will take over the on-premise version. There are many benefits to the SaaS service. Some of these include automatic updates, universal accessibility, and strong security.
Besides, cloud-based models will be beneficial to SMEs. They will be able to reap the benefits of enterprise-wide ERP solutions without making significant IT spending.
3. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT connects physical devices or sensors over the same network and enables these devices to exchange data without human intervention. Connecting IoT with ERP will open gates of opportunities. It will make an ERP solution intelligent and flexible.
Enterprise Software Related Research Articles:
- VAT in Gulf: How Cloud ERP Software Can be a GameChanger
-
Track and Record Business Assets by using ERP Software in UAE
-
How To Use ERP Software for Getting the Most Out Of Your Investment?
-
Tips & Tricks for Selecting the Right ERP System for Your Business
-
ERP vs. Accounting Software – What are The Major Differences?
-
eCommerce ERP Integration – Benefits, Challenges and Best Practices
-
ERP for Logistics and Distribution Companies : A Definitive Guide
-
ERP in Production Planning: The Future of Manufacturing Industry
-
ePROMIS vs. Oracle Fusion vs. Oracle Netsuite vs. SAP S4HANA vs. Microsoft Dynamics 365



.png)