The E-way bill system is a revolutionary tool that has been implemented by policymakers to curb tax evasion across the country. E-Way is basically an electronically make bill for the movement of goods, and it is created on the E-Way Bill Portal. On the other hand, an E-Way bill can also be generated through an SMS facility, specialized Android applications, and by site-to-site integration – making it highly convenient and flexible for users.

It is a very important document that an individual in charge of a conveyance transporting any consignment of goods worth a value exceeding Rs 50,000 is required to generate.
It is an obligatory document that is created from the GST Common Portal by registered transporters who regularly undertake the movement of goods. Any transporter who is carrying goods across India needs to adhere to the E-Way document as it is mandatory under Indian law.
The main objective of the E-Way bill system is that it will greatly boost up GST compliance across the country and will ensure that the taxation system remains fair and structured in case of movement of goods throughout the country.
Who needs to generate an E-Way Bill? What are the basic criteria required and the right time to generate it?
It is absolutely essential that any transporter who commences the business of carrying material goods should be aware of the regulations related to creation. It can be generated by the following:
-
Registered Person
It is compulsory to generate it when there is authorized the movement of goods above the value of Rs. 50,000 to or from a registered individual.
-
Unregistered Person
Unregistered persons also need to generate e-Way bills if they are carrying out transporting operations. Yet, when a supply transaction is completed by an unregistered person to a registered individual, the recipient will need to ensure that all the requisite compliances are adhered to and all documentation is in order.
-
Transporter
Any transporter carrying a consignment of goods by air, rail, or freight also needs to generate an E-Way bill if the document has not been prepared by the supplier.
The mandatory implementation of this E-Way Bill system will be commenced from the 1st of April, 2018, and is applicable to the movement of goods from one state to another. All the states will be divided into four categories, and it will be implemented in a phased manner from 15th April 2018 to 1st June 2018. The E-Way Bill system under the new GST rules has replaced the previous Way of billing and is now an electronically generated document.
How is the E-Way bill generated?
Large-sized global business organizations or big-scale logistic operators that have many consignments traveling across the country on any single day definitely need a simple, well-structured, and time-saving method to generate all their required E-Way bills. Since the new bill is an electronic document that needs to be carried by transporters for the movement of any kind of goods, it can be generated in a highly automated manner through a number of transport software suites.
There are various advanced and sophisticated E-way bill ERP software systems that provide a seamless gateway for registered taxpayers and transporters, that they can follow a simple procedure to generate a valid E-Way bill.
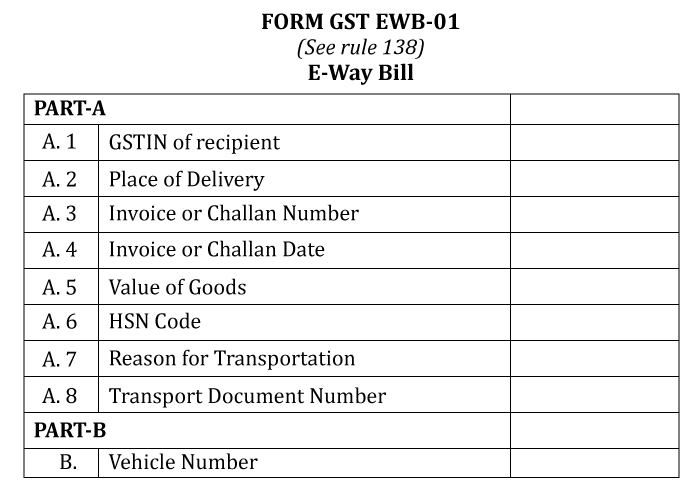
The E-Way bill can be generated through the portal – all it requires is a valid login ID. It can be generated by a registered person who is a consignor or recipient of goods by providing the required information in Part B of Form GST EWB 01.
It is the responsibility of the transporter or person in charge of moving the goods to make sure that all the formalities related to completed on time and efficiently. The transportation system is a major overhaul in the traditional taxation structure of India – its implementation will definitely encounter some major operational challenges. Adopting customized billing software is surely an efficient solution that makes sure that your E-Way billing transactions occur seamlessly.
Which states have implemented the E-Way Bill System across India?
The E-Way bill system is being implemented in a phased and regulated manner across the country to avoid any kind of disruption in transport activities. The following states in India have implemented it in totality and made it compulsory for inter-state transport or movement of goods:
- Karnataka
- Uttarakhand
- Rajasthan
- Kerala
The rest of the 25 states and 7 union territories of India have decided to join the league on a trial basis till 31st January, and later make it a mandatory law to generate for movement of goods.
There are 13 states in India that have agreed to commence E-Way Bills for the cross-movement of goods with effect from 1st February 2018. These states are:

As per the latest 26th GST council meeting, it has been decided that the complete inter-state implementation of the E-way bill system will be adopted from 1st April 2018. The meeting also finalized that the intra-state implementation of the mandatory system will be kick-started from 15th April in a gradual and phased manner. All the states will be divided into four major categories for the complete implementation of the E-Way bill regulation.
What are the rules and the various documents required for generating the E-Way bill?
It is a highly official and important electronic certificate; hence there are certain documents that need to be produced to generate a valid E-Way bill. It is absolutely essential to submit authorized copies of these documents otherwise the E-Way bill will not be valid as a legal certificate for the movement of goods.
Here is a list of the important documents required to generate the E-Way bill:
- A detailed invoice or complete bill of supply or the delivery challan.
- A copy of the E-Way bill or the E-Way bill number – either as a physical document or mapped to a radio frequency identification device (RFID) that is embedded in the conveyance of transport in such a manner that may be notified to the commissioner.
- If the transport is occurring by road, then a registered transporter ID or vehicle number is.
- If the conveyance is occurring through air, rail, or ship –the transporter ID, main transport number, and the date of the document is required.
It is compulsory to make sure that these documents are in order and submitted for the electronics to be valid and authorized for the movement of goods across the country. Document management software can certainly help you with this.
What is the value of the consignment of goods in the E-Way bill?
It is very important to keep in mind the value of the consignment of goods for the accurate generation of it. The value of the consignment of goods can be explained as follows:
- The invoice value exceeds a sum of Rs. 50,000, or
- If a vehicle is carrying goods under multiple invoices, then the sum total aggregate invoice value exceeds Rs. 50,000.

In case either of the above two points is satisfied, the user must generate a valid E-Way bill for the transport of goods across the country. For the purpose of an E-Way bill, invoice value can be understood as the total transaction value per invoice that is inclusive of all the taxes and exempts any goods that are being carried along the taxable goods and are billed together for the calculation of the E-Way bill amount.
Points to Keep in Mind Regarding E-way Bill System
The Validity of the E-Way Bill
There are various conditions that have to be followed to ensure that the generated is a valid document. Here are some important aspects that need to be kept in mind to ensure that it is valid across India:
- An E-Way bill for a distance of less than 100 km shall be valid for a period of one day or 24 hours from the relevant date.
- After the first 100 km, for every additional 100 km or part thereof, the validity period will increase by one more day.
This validity is applicable for all transporters barring the case of over-dimensional cargo, as there are different rules in those specific cases:
- In the case of over-dimensional cargo for a distance of fewer than 20 km, the E-Way bill shall be valid for a period of one day from the relevant date.
- For every additional 20 km or part thereof, the validity will increase by one more day in case of over-dimensional cargo.
There is another provision for extending the validity of the E-Way bill also. The generator of the E-Way bill can extend the validity period if all formalities are completed four hours prior to the original expiry of the bill. This makes it possible for transporters to ensure the continued validity of the E-Way bill.
Cases Where the Implementation of E-Way Bill System is Not Required
There are certain cases where the E-Way billing system is not compulsorily required such as:
- The main mode of transport is a non-motor vehicle.
- The goods are transported from the main customs port, airport, air cargo compound, or inland customs station to the inland container depot (ICD) or container freight station (CFS) for proper clearance by customs.
- The goods are being transported under customs supervision or the customs seal.
- The goods are being transported through customs bond from ICD to the customs port or from one major custom station to another.
- The transit cargo is being transported to or from the countries of Nepal or Bhutan.
- The cargo containers that are being transported are empty.
- The movement of goods is for military purposes under the Ministry of Defense.
- The transporter is moving goods to or from between the place of business and a weight bridge for weighment at a distance of 20 km, supplemented by a Delivery challan.
- The goods are transported by railways where the main consignor of goods is the Central Government, State Governments, or a specific local authority.
- The goods that are being transported are exempt from requirements according to the State/ Union Territory GST rules.
The Responsibility and Liability For The Transporter In E-Way Bill System:
The system is very well-structured and there are certain important responsibilities/liabilities that have to be undertaken by the transporters for its efficient functioning:
- Any transporter who is carrying certain goods by road, air, rail, or ship is also needed to generate E-Way Bill, even if the supplier has not created an E-Way Bill due to any particular reason.
- The transporter has to be electronically generated on the basis of accurate information that is shared by the suppliers or consignors concerning the Invoice/challan.
- If the main transporter does not generate an E-Way bill according to the mandatory legal requirements, he may face a heavy penalty of Rs 10,000 or the tax amount sought to be evaded – whichever amount is greater and also be further liable for the complete confiscation of goods and seizure of the transport vehicle.
Bottom Line
The E-way bill system is indeed a dynamic and transparent approach that can greatly control tax evasion all across India. It is definitely the best way to increase GST compliance in case of the movement of goods in the country, creating a fair and well-structured system that is functional, practical, and flexible for users.
SoftwareSuggest empowers businesses to discover top business software and service partners. Our software experts list, review, compare and offer a free consultation to help businesses find the right software and service solutions as per their requirement. We have helped 500,000+ businesses get the right software and services globally. Get a free consultation today!



